Do you know what catarrh is? Ague? How about Dropsy? Apoplexy? Consumption? Scrofula?
While doing research on South Whidbey residents prior to 1920, we have sometimes come across such terms in their obituaries or on their death certificates.
We thought we would share some of the definitions for these outdated terms describing medical conditions as well as some of the prolific patent medicine for symptoms such as ‘torpid bowels’ and electricity ‘cures’ for ‘men’s weakness’ that were prevalent in the newspapers.
————–
AGUE: malarial infection characterized by paroxysms (stages of chills, fever, and sweating at regularly recurring times) and followed by an interval or intermission of varying duration. Popularly, the disease was known as “fever and ague”, “chill fever”, “the shakes.” Ague cake is a hardening of the spleen caused by malaria.
APOPLEXY: paralysis caused by stroke.
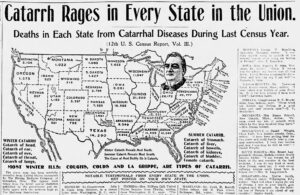
CATARRH: inflammation of a mucous membranes of the head and throat, with a flow of mucous. Bronchial catarrh was bronchitis; suffocative catarrh was croup; urethral catarrh was gleet; vaginal catarrh was leukorrhea; epidemic catarrh was the same as influenza. Synonyms: cold, coryza. Catarrhal bronchitis is acute bronchitis.
CONSUMPTION: a wasting away of the body; formerly applied especially to pulmonary tuberculosis, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium TUBERCULOSIS.
DROPSY: a swelling caused by accumulation of abnormally large amounts of fluid. Caused by kidney disease or congestive heart failure. An anascara, a species of dropsy, is an extravasation of water lodged in the cells of the membrana adiposa.
GRAVEL: a disease characterized by small stones which are formed in the kidneys, passed along the ureters to the bladder, and expelled with the urine.
GRIPPE: influenza, also La Grippe or grip.
LUMBAGO: A rheumatic condition of the loins (the sides of the body and back below the ribs and above the pelvis)
MIASMA: “poisonous vapors” (bad smells) that were believed to spread infection.
MILK FEVER: from drinking infected milk, such as undulant fever or brucellosis.
PINK DISEASE: disease in children caused by mercury poisoning from the use of mercury salts in teething powders.
PUERPERAL FEVER: a fever arising after giving birth, also called child bed fever, caused by bacterial infection and commonly fatal until the introduction of sulphonamides and later antibiotics in the middle of the 20th century.
QUINSY: an acute inflammation of the soft palate around the tonsils, often leading to an abscess. Synonyms: suppurative tonsillitis, cynanche tonsillaris, paristhmitis, sore throat.
SCARLATINA: Scarlet Fever, a contagious disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes, which attacks the red blood cells and produces inflammation of the nose, throat and mouth, headache, sickness and red rash.
SCROFULA: tuberculosis of the lymphatic glands, especially those in the neck. A disease of children and young adults.
TYPHUS: An acute, infectious disease caused by the parasite Rickettsia prowazekii, transmitted by lice and fleas. It is marked by high fever, stupor alternating with delirium, intense headache and dark red rash. The epidemic or classic form is louse borne; the endemic or murine is flea borne. Synonyms: typhus fever, malignant fever (in the 1850s), jail fever, hospital fever, ship fever, putrid fever, brain fever, bilious fever, spotted fever, petechial fever, camp fever, camp diarrhea.